There has been a lot of talk about the unstructured data since the conversation around big data started or shall we say that one of the reason of big data’s existence is the introduction and incorporation of unstructured data and its overlay onto the ever existing structured data. But a million dollar question is “What is Unstructured Data?”. So lets spend sometime clarifying the myths around unstructured data and how it is being leveraged by various organizations.
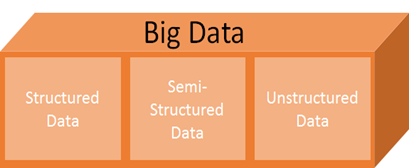
The variety component of Big Data talks about utilizing various data types. So, Big Data has the following data components:
- Structured Data
- Semi-Structured Data
- Unstructured Data
But before we get into exploring the Unstructured data. Let us very quickly talk about structured data, as it all started with the structured data.
|
| Structured data was always there. Every organisation is sitting on piles of structured data in various divisions stored in normalised / denormalised formats stored in:
|
The structured data sources have defined data types, structures, have linkages to allow for joins, etc.
Most of the organisations are structured data havens as just these data points are found in multiple data sources in large volumes within the organisation and are not tapped. Data warehouses were built till recently to help tap the information hidden in these multiple sources.
|
| With the Social Media coming into play, Semi-structured data became a talking point. Mostly data coming from Facebook, Twitter, Blogs, publically available websites, etc. makes the basis of semi-structured data. These data sources usually have a defined structures and mostly contain text information. |
e.g. Twitter has the following structure:
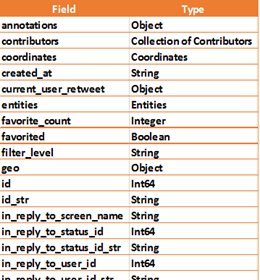
The data stored in these fields is then utilised / mined using various techniques to enhance / enrich the structured data.
Hence, the social data has a defined structure.
The free flow text generated through the social media is the only unstructured component whilst the remaining data is structured.
Most of the times, the social data is mistaken with unstructured data. The social data is NOT unstructured data, it is semi-structured and in fact, some of the social data contains industry standard structures.
|
| As the name suggests, Unstructured data are the data sources that does not have any structure. Unstructured data does not have any defined, consistent fields and it may even do not have any numbers and text. |
Some type of Unstructured data contain:
| Voice Data |  | Human Voice data collected through phone calls, conversations, etc. |
| Image Data |  | Facial Images, landscape images, x-ray images, etc. |
| Videos Data |  | Video content generated during events and other regular CCTV footage |
| Machine Data |  | Data generated through cars, ships, mobile phones, etc.. |
Let us explain each of the above data sources in detail.
 Voice data:
Voice data:
Human voice contains a lot of information and it needs access and mined. The spectrogram of the human voice reveals its rich harmonic content including pitch, tone, emotion, bass, etc. which can be decoded and mined to understand the customer behaviour and help address their concerns to avoid churn, retain and identify fraud, to start with.
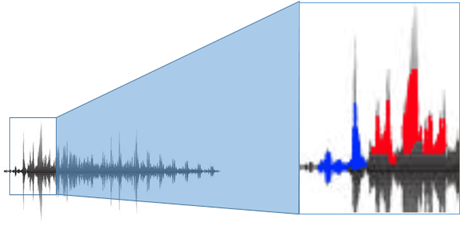
There are lot of software / hardware applications that can find out the emotions, sentiment, identify the individual by matching voices with the sample, determining age, etc. Some of the applications are military grade and are similar to the technology used at the times of war.
Voice Data Use Cases:
- Some organisations are using the voice data to identify customers to avoid asking multiple questions before allowing the customers to access their information. This provides a very good customer experience and reduces customer annoyance.
- One large bank is using the voice data to identify customers who can commit fraud by running predictive model on the voice profile.
- One large Telco is using the call conversation to calculate the sentiment / NPS of the customer in real time.
 Image Data:
Image Data:
Total number of pictures taken in last 5 years is more than double the pictures taken in 1900 -2000. This gives us an opportunity to use patterns within the pictures and mine the information available to us.
Various techniques like pixilation, pattern matching, image processing, feature extracting, etc. allows us covert the pictures into data and further mine it using classification algorithms.

Image Data Use Cases:
- One of the most common use case is the thumb print recognition which is now available in our phones.
- Police force and several other Security agencies use image mining techniques to identify potential terrorism candidates by understanding their image patterns.
- One large bank is using the image mining technique and predicting likelihood of a customer to be fraud
 Video Content Data:
Video Content Data:
Video content contains temporal and spatial events and it can be seen as automated equivalent to the biological visual cortex.
Video Motion Detection is one of the simpler forms where motion is detected with regard to a fixed background scene. More advanced functionalities include video tracking and egomotion estimation.
Based on the internal representation that video content data generates in the machine, it is possible to build other functionalities, such as identification, behaviour analysis or other forms of situation awareness.
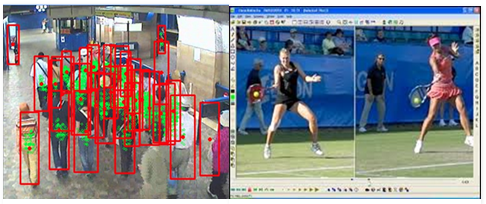
Video Content Use Cases:
- Various sports have been using the video analysis techniques for a few years to:
- Improve player performance
- Provide analysis to the viewers
- One very large security agency uses the video data to identify trouble making candidates in the premise by using predictive analysis based on the sequence of actions performed by the individual.
- A very large retailer in the US is using Video Content data to not only count the floor footfall, most occupancy areas in the store but also identify customers and link them back to their online behaviour to get a 360 view of their activities.
 Machine Data:
Machine Data:
As the size of computer chips is reducing, there is potential of having a computer chip in almost all the machines, e.g. cars, the mobile phones, ships, etc.
The data residing in these machines is unstructured and is not of a standard format to be available for mining. This unstructured data is being extracted by large organisations and then used to understand the hidden patterns to drive efficiency.

Machine Data Use Cases:
- A large car company is collecting data from the cars to understand the reason behind engine failure to optimise the performance and reduce engine failure possibilities.
- A large Telco in the US is using mobile app data to advertise and promote retail offers by understand customer behaviour.
- The multiple machine data sources are used by Google to build its first self-driving car – Google Autonomous Car.
Conclusion:
There was always large volumes of data lying in any organisation which was not tapped and IT teams were trying for years to get that data available to the business. With big data platforms, it is now possible to not only get access to the internal data but overlay the internally available structured data with the unstructured data.
To be successful, the technologists and the big data evangelists must first create strong use cases and plan the roll out of the big data platform to focus on business value.
This opens the discussion around Big Analytics, but that is a topic in itself.